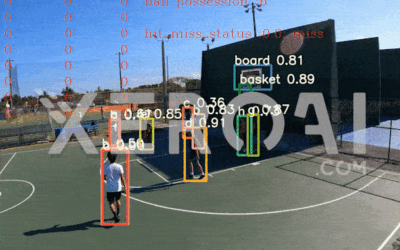
In the world of sports, understanding the intricacies of player performance and game strategy is paramount to success. Volleyball, a high-speed and strategic sport, is no exception. With the advent of deep learning and camera-based solutions, the way we analyze volleyball players and matches is undergoing a transformation. In this blog, we’ll take you on a journey through the world of volleyball analysis powered by cameras and deep learning algorithms. From player actions to game strategy, this technology is reshaping the way we perceive and improve volleyball performance.
1. The Benefits of Volleyball Analysis Using Cameras
Analyzing volleyball using cameras as the primary tool for analysis offers several significant advantages over traditional methods. Unlike sensors that need to be attached to players or equipment, cameras provide a non-invasive and cost-effective solution. Let’s explore some of the benefits:
1.1. Player Performance Metrics:
Cameras can capture detailed player performance metrics, including serving accuracy, ball placement, and movement patterns. These insights help players identify their strengths and areas for improvement, leading to more effective training and performance enhancement.
1.2. Match Strategy:
Coaches can analyze match footage to develop effective strategies for upcoming opponents. They can study player tendencies, preferred shots, and court positioning. This deep understanding of the game helps teams formulate winning strategies and adapt to their competitors’ playing styles.
1.3. Real-Time Feedback:
During practice sessions and games, real-time feedback from cameras allows players to make immediate adjustments to their technique and strategy. This instant feedback loop enhances the learning process, leading to rapid skill development and improved on-court performance.
1.4. Injury Prevention:
By closely analyzing player movements, coaches and trainers can identify potential injury risks and implement preventive measures. Understanding how players move and react on the court enables the development of injury prevention programs that focus on specific areas of concern, reducing the likelihood of injuries.
1.5. Tactical Insights:
Cameras provide a comprehensive view of the entire volleyball court, allowing teams to gain tactical insights into their opponents’ strategies and weaknesses. Coaches can identify patterns in opponents’ plays and devise counter-strategies to gain a competitive advantage.
1.6. Team Coordination:
Cameras capture the dynamics of team play, helping coaches evaluate the effectiveness of coordinated plays, such as serves, spikes, and blocks. This analysis fosters better teamwork and communication among players, leading to improved overall performance.
1.7. Objective Evaluation:
Camera-based analysis provides an objective evaluation of player and team performance. It eliminates subjective biases and allows for fair and accurate assessments, creating a level playing field for athletes and teams striving for excellence.
1.8. Fan Engagement:
The use of cameras in volleyball analysis also enhances the fan experience. Fans can enjoy more in-depth analysis and insights into their favorite teams and players. Video footage from cameras adds excitement and engagement to broadcasts, drawing more viewers to the sport.
2. Use Cases and Analysis Aspects in Volleyball
Volleyball analysis using computer vision and deep learning opens up a world of possibilities for enhancing player and team performance. Here are the primary use cases and analysis aspects in volleyball:
2.1. Serve Analysis:
Cameras can track various aspects of the serve, providing valuable insights to players and coaches:
2.1.1. Serve Speed:
Measure the velocity of the serve to assess its power and effectiveness.
2.1.2. Serve Placement:
Analyze where the serve lands in the opponent’s court to strategize placement.
2.1.3. Serve Spin:
Evaluate the spin on the ball, which can affect its trajectory and bounce.
2.1.4. Ace Count:
Keep track of the number of aces achieved with serves.
2.1.5. Service Errors:
Monitor the occurrence of service errors, including faults and missed serves.
2.2. Attack and Block Analysis:
Understanding offensive and defensive plays is crucial for success in volleyball:
2.2.1. Attack Success Rate:
Determine how successful a player or team is at scoring points through attacks.
2.2.2. Block Success Rate:
Assess the effectiveness of blocking against opponent attacks.
2.2.3. Attack Variety:
Analyze the types of attacks used, such as spikes, tips, and roll shots.
2.2.4. Blocking Techniques:
Evaluate the blocking techniques employed by players, including single blocks, double blocks, and timing.
2.3. Digging and Passing:
The ability to dig and pass effectively is essential for receiving and setting up plays:
2.3.1. Dig Success Rate:
Measure how often players successfully dig the opponent’s attacks.
2.3.2. Pass Accuracy:
Assess the accuracy of passes, ensuring they reach the intended target for setting.
2.3.3. Reception Quality:
Evaluate the quality of receptions, which are crucial for setting up offensive plays.
2.4. Player Movement and Positioning:
Tracking player movements is fundamental to optimizing positioning on the court:
2.4.1. Player’s Court Coverage:
Determine how effectively players cover their designated areas on the court.
2.4.2. Distance Covered:
Analyze the distance covered by players during a match, helping to evaluate their endurance and fitness.
2.4.3. Movement Efficiency:
Assess the efficiency of players’ movements, including lateral and forward-backward transitions.
2.5. Rally Analysis:
Analyzing rallies provides insights into overall team dynamics and performance:
2.5.1. Length of Rallies:
Measure the duration of rallies to assess players’ endurance and ability to maintain rallies.
2.5.2. Point Conversion:
Track the number of successful points scored within rallies.
2.5.3. Error Analysis:
Identify unforced errors and their impact on rally outcomes.
2.5.4. Average Rally Duration:
Calculate the average duration of rallies in a match.
2.6. Opponent Analysis:
Understanding the opposition’s playing style is critical for devising effective strategies:
2.6.1. Study of Playing Style:
Analyze the opponent’s preferred tactics, including types of attacks and defensive strategies.
2.6.2. Strengths and Weaknesses:
Identify areas of strength and weakness in the opposing team’s gameplay.
2.6.3. Preferred Shots:
Determine the types of shots commonly used by opposing players.
2.6.4. Court Positioning:
Assess where opponents tend to position themselves during different phases of the game.
3. Action Tracking for Volleyball
Volleyball analysis using computer vision and deep learning involves tracking various actions and performance metrics to gain valuable insights into player and team dynamics. Here are the key action tracking elements for volleyball:
3.1. Point Analysis:
3.1.1. Number of Points Won:
Total number of points won by the team.
3.1.2. Number of Points Lost:
Total number of points lost by the team.
3.1.3. Points Won on Serve:
Points won when the team is serving.
3.1.4. Points Won on Return:
Points won when the team is receiving.
3.2. Ace Count:
3.2.1. Number of Aces Served:
Count of serves that result in aces (unreturnable serves).
3.3. Double Faults:
3.3.1. Number of Double Faults:
Count of serves that result in double faults (failed serves).
3.4. Net Approaches:
3.4.1. Number of Times Approached Net:
Count of times a player approaches the net.
3.4.2. Success Rate at the Net:
Percentage of successful net approaches.
3.5. Break Points:
3.5.1. Number of Break Points Faced:
Count of situations where the team is at risk of losing their service game.
3.5.2. Number of Break Points Converted:
Count of situations where the team successfully breaks the opponent’s serve.
3.6. Serve and Return:
3.6.1. Serve Speed and Placement:
Details of the serve, including maximum serve speed, serve placement (wide, T, body), and variations between 1st and 2nd serves.
3.6.2. Return Accuracy:
Assessment of return accuracy, including the number of returns in play and return winners.
3.7. Net Play:
3.7.1. Net Points Won:
Count of points won at the net during volleys and smashes.
3.7.2. Volley Success Rate:
Percentage of successful volleys.
3.7.3. Smash Success Rate:
Percentage of successful smashes.
3.8. Fitness and Health:
3.8.1. Heart Rate Monitoring:
Monitoring a player’s heart rate during the match to gauge their physical exertion and fatigue levels.
3.8.2. Injury Prevention:
Analyzing player movements to identify potential injury risks and monitoring body mechanics to prevent injuries.
3.9. Court Positioning:
3.9.1. Position on the Court:
Tracking a player’s position on the court during rallies to understand preferred court areas and court coverage strategies.
4. Data Collection and Camera Placement in Volleyball Analysis
In volleyball analysis using computer vision and deep learning, data collection relies on strategically positioned cameras. Camera placement is crucial to capture comprehensive footage without missing critical details. Here’s how to set up cameras for effective volleyball analysis:
4.1. Court Coverage:
Cameras should be strategically placed to capture the entire volleyball court, ensuring that no part of the action is missed. It’s important to minimize interference from the audience to maintain a clear view of the game.
4.2. Distance from Court:
Cameras should be positioned at an optimal distance from the court, striking a balance between capturing players’ actions accurately and ensuring a wide field of view. This distance will vary depending on the camera’s capabilities and the size of the court.
4.3. Angle:
Avoid a bird’s-eye view perspective, as it can make player identification challenging. Instead, opt for side views or slightly elevated angles that offer a clear line of sight to the players and the ball.
4.4. High-Resolution Cameras:
The use of high-resolution cameras is crucial for capturing fine details, such as ball trajectory, player movements, and facial expressions. Higher resolution enables more precise tracking and analysis.
4.5. Multiple Angles:
To provide a comprehensive view of the game, consider using multiple cameras from different angles. This multi-angle approach enhances player tracking and ensures that no important action is missed during the match.
4.5. Camera Stability:
Stable cameras are essential to prevent image blurring and ensure consistent tracking. Mounting cameras securely and minimizing vibrations or movement is vital for clear and sharp footage.
4.6. Lighting Conditions:
Adequate lighting is necessary to capture clear and well-defined images. Proper lighting helps maintain high-quality footage and ensures that players and the ball are easily distinguishable.
4.7. Camera Calibration:
Calibrating the cameras correctly is essential for accurate measurement of player positions and distances. Proper calibration takes into account lens distortion and perspective, ultimately improving the system’s tracking accuracy.
5. Conclusion
The benefits of volleyball analysis using cameras are multifaceted and far-reaching. From providing players with critical performance metrics to aiding coaches in devising winning strategies, this innovative approach has redefined how we perceive and improve the game.